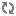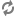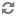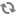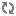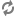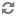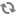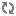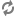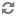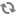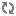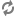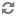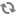Some Thais see economic hardship as a boon to traditional values
·期刊原文
Some Thais see economic hardship as a boon to traditional values.
by Yvan Cohen
Christian Science Monitor
Vol. 90 No. 168 1998.07.24
P.7
Copyright by Christian Science Monitor
"This crisis is great," insists Abbot Pra Payom Galyano, as he adjusts his
saffron robe in the torpid afternoon heat at a temple near the Thai capital
of Bangkok. "It is going to force people to go back to the traditional
lifestyle. They had lost their way."
Forget the mismanagement, nepotism, and corruption that economists
typically blame for Thailand's economic crash: The real problem, say a
growing number of Thais, is the decline in Buddhist morality.
"The basis of the crisis is that people did not follow the teachings of the
Lord Buddha," affirms American-educated Thai businessman Charoen-Rajapark.
"We focused on productivity and not on righteousness."
This nation of 60 million groans under the weight of a $90 billion external
debt. The economic collapse has thrown one of the world's fastest-growing
economies into a free fall. The resulting hardship from the recession and
its attendant social ills (such as widespread drug abuse) that are now
often associated with the boom years, have prompted nationwide soul
searching.
'Awakening old values'
In weekly TV broadcasts, senior monks explain problems from a Buddhist
perspective.
"Monks are using the crisis to awaken people to old values," says Bruce
Evans, an Australian scholar who was a Buddhist monk for 17 years. "They're
telling their followers that it's time to get back to basics."
"The current decline in morality is a side effect of industrialization,"
adds Khun Payong, a retired teacher who has set up "morality camps" for
young Thais. "We should go back to our old traditions and not depend so
heavily on material things."
The call for a return to homespun values, self-reliance, and Buddhist
morality also carries undertones of nationalism.
"Don't sell off the country. Join together to protect our nation and keep
it for our children," reads a campaign sticker distributed by Abbot Pra
Payom. "Foreigners are benefiting from our misfortune," he complains, a
reference to the influx of overseas investors hunting for bargains in
Thailand.
Another popular monk, Abbot Luang Ta Maha Bua, made the most of the
nationalist mood by undertaking a headline-grabbing "Help the Country"
campaign. It drew in donations worth $1.2 billion to help pay off
Thailand's massive national debt.
But if the crisis has provided an opportunity for monks and temples to put
Buddhist compassion into practice, it has also prompted a closer
examination of the quality of the Thai monkhood as an institution. Some
critics complain that instead of tempering materialism, Thailand's
monasteries have themselves been tainted by it.
"Subconsciously, during the boom, people were encouraging monks toward
materialism," Mr. Evans, the former monk, says. "Because the population
became wealthy, and people made donations, the monasteries became wealthy,
too."
One social critic, newspaper columnist Sanitsuda Ekachai, puts it in
starker terms. The decline in standards among monks is a result of the
"commercialization of Buddhism," she says. In a recent article in the
Bangkok Post, Mrs. Ekachai described how one monk set up a "holy-water
supermarket" that sold 200 brands of bottled water from well-known monks
nationwide.
Khun Premrudee Puyongyuth, who lost her job in a supermarket and now sells
herbal medicines at Pra Payom's temple, also blames the monasteries for
"setting a bad example. "Some temples competed with each other to build the
biggest or the most famous temple," she says. "If the abbot is focusing on
amassing fame and fortune, his followers will act in the same way."
'This is our opportunity'
The view that the monkhood is in need of reform has even reached the desks
of Thailand's policymakers. Last month, the director general of the
country's Religious Affairs Department, Samanchit Piromruen, called for a
halt on construction of new temples. The department says it wants to
lighten the financial burden on congregations during the economic slump.
Some argue that Buddhism and capitalism will never fit together easily. "I
see a connection between the boom and the general decline in Buddhist
values," Evans notes. "Material growth is based on unspiritual values."
But others, like social activist Sulak Sivaraksa, see the crisis as a kind
of time out from profitmaking, a way to refocus on what is really
important.
"Now we can make use of Buddhism. This is our opportunity to do something,"
he says.
PHOTO (COLOR): TRADITION MEETS CAPITALISM: A Buddhist monk stands in a lot
full of cars being sold by the formerly wealthy in Bangkok. Monks
themselves have been criticized for becoming too materialistic during
Thailand's boom years
欢迎投稿:lianxiwo@fjdh.cn
2.佛教导航欢迎广大读者踊跃投稿,佛教导航将优先发布高质量的稿件,如果有必要,在不破坏关键事实和中心思想的前提下,佛教导航将会对原始稿件做适当润色和修饰,并主动联系作者确认修改稿后,才会正式发布。如果作者希望披露自己的联系方式和个人简单背景资料,佛教导航会尽量满足您的需求;
3.文章来源注明“佛教导航”的文章,为本站编辑组原创文章,其版权归佛教导航所有。欢迎非营利性电子刊物、网站转载,但须清楚注明来源“佛教导航”或作者“佛教导航”。
下一篇:Italian Studies on Far Eastern Thought in Comparative Philosophy